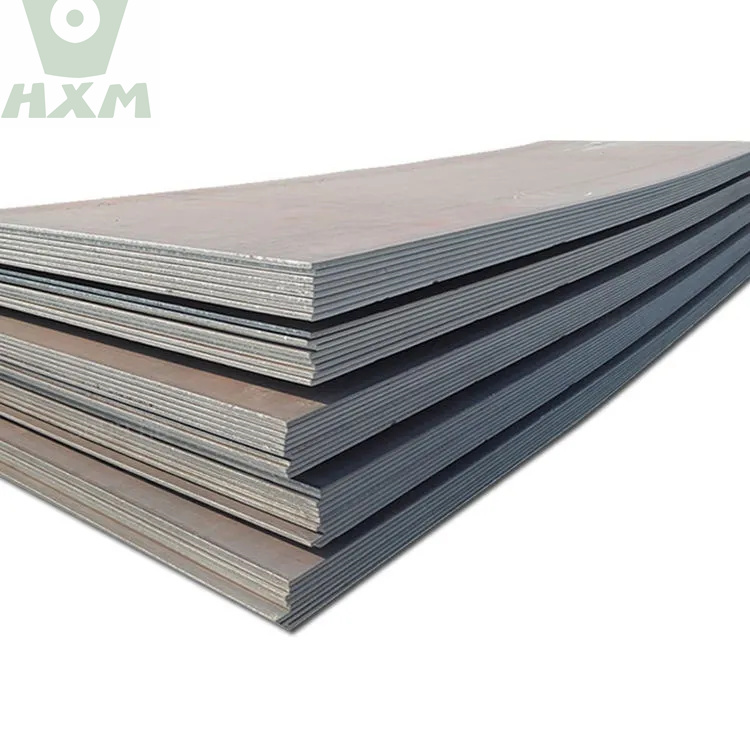
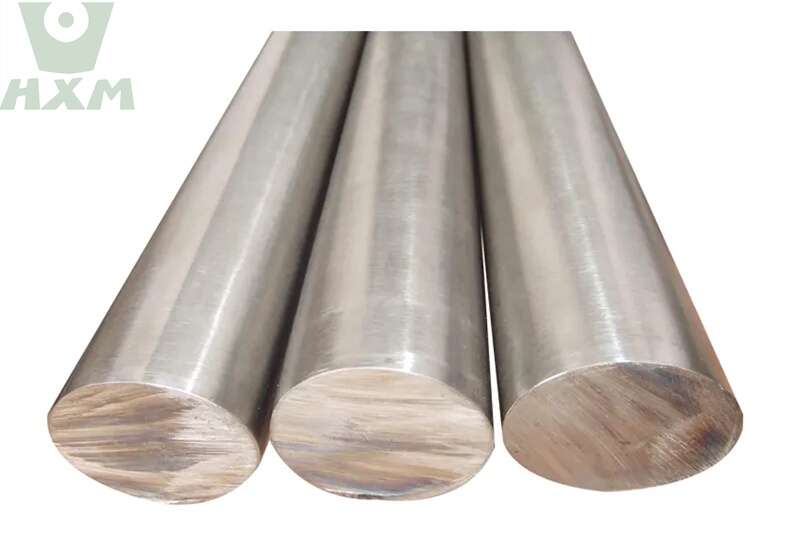
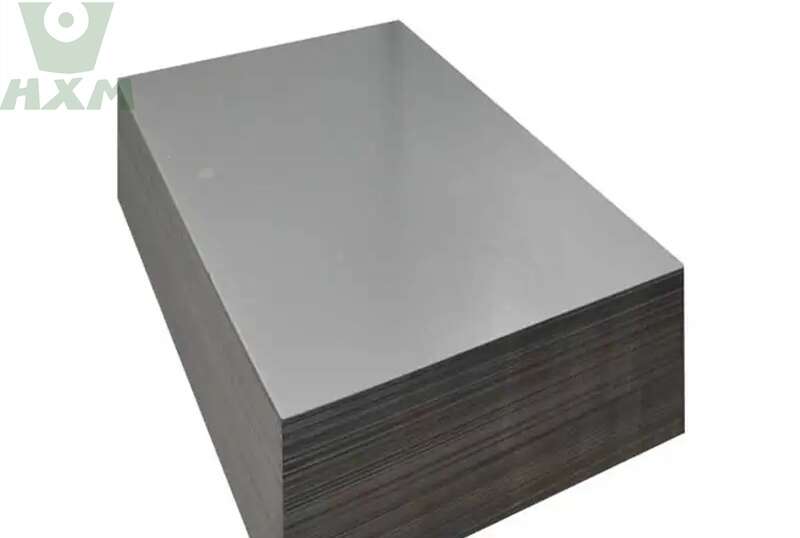
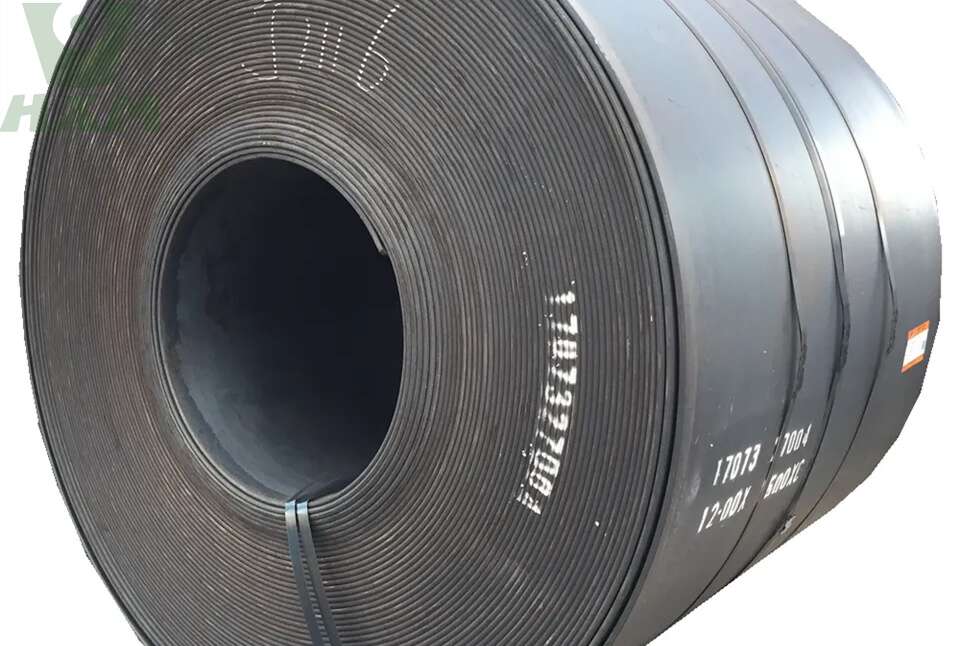
Alloy Steel
Huaxia-steel is a leading B2B company based in Shanghai, China, specializing in the export of alloy steel products. With years of experience in the industry, we have built a reputation as a reliable and trustworthy supplier for our global clients, who are mainly professional metal procurement specialists. Our extensive product range includes a wide variety of alloy steel products, including bars, plates, sheets, coils, pipes, and fittings, all made from high-quality materials and manufactured to meet international standards.
At Huaxia-steel, we pride ourselves on our professionalism and dedication to providing the best possible service to our clients. Our team of experts works closely with our clients to understand their unique needs and specifications, and we strive to provide customized solutions that meet their exact requirements. We are committed to ensuring the highest quality of our products through strict quality control processes, and we always strive to exceed our clients’ expectations in terms of product quality, delivery times, and customer service.
We understand that our clients’ success depends on their ability to source high-quality materials at competitive prices, and we are committed to helping them achieve their goals. With a focus on reliability, transparency, and integrity, we have built long-lasting relationships with clients all over the world, who trust us to deliver on our promises. When you work with Huaxia-steel, you can be sure that you are working with a partner who understands your business and is dedicated to helping you succeed.
Alloy Steel Plate

medium carbon alloy steel
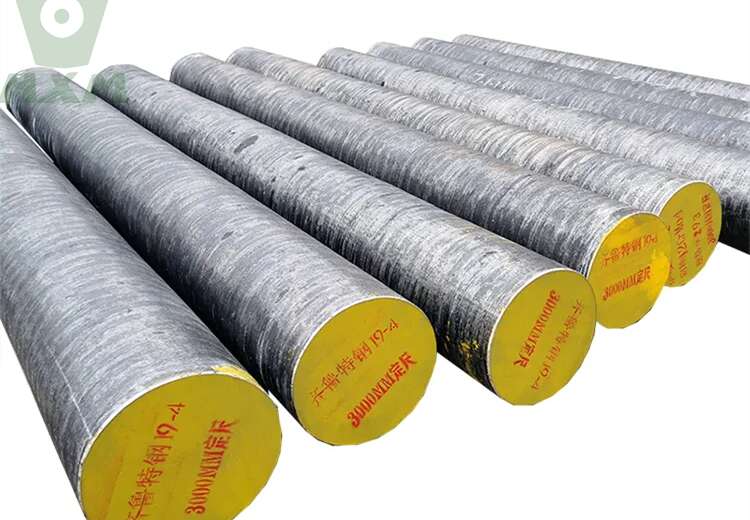

low carbon alloy steel

high carbon chromium steel

medium carbon alloy steel

low carbon alloy steel
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
All You Need To Know About Alloy Steel
Alloy steel is a type of steel that contains additional elements to improve its properties, such as strength, hardness, corrosion resistance, and more. These elements can include manganese, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, vanadium, and others.
Alloy steel is commonly used in various industrial applications, including construction, automotive, aerospace, and more. It offers superior mechanical properties compared to carbon steel, making it a popular choice for high-stress applications. When selecting alloy steel for your specific application, it’s important to consider factors such as the required strength, corrosion resistance, and temperature resistance.
At Huaxia-Steel, we offer a wide range of alloy steel products that can be customized to meet your unique needs. Contact us today to learn more about our alloy steel offerings.
What is alloy steel?
Alloy steel is a type of steel that contains other elements besides iron and carbon, which are the main components of standard carbon steel. These additional elements, such as chromium, nickel, or molybdenum, are added to improve the steel’s mechanical properties, such as strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance.
Alloy steel is commonly used in the manufacturing of industrial equipment and machinery, such as pipelines, construction materials, and automotive components, due to its durability and resistance to wear and tear. Compared to carbon steel, alloy steel can withstand higher stress and pressure, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications.
At Huaxia-steel, we specialize in exporting high-quality carbon steel products, including alloy steel, to customers worldwide. Our extensive selection of alloy steel products meets international standards and specifications, ensuring that our customers receive reliable and high-performing products that meet their exact requirements.
What is low alloy steel?
Low alloy steel is a type of steel that contains a small amount of additional alloying elements, typically less than 5% of the total composition by weight.
These additional elements can include chromium, nickel, molybdenum, or vanadium, among others. The primary purpose of adding these elements is to improve the mechanical properties of the steel, such as strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance.
Compared to standard carbon steel, low alloy steel has better mechanical properties, making it ideal for applications that require high strength, such as in the construction of heavy equipment or machinery. Low alloy steel can also offer better resistance to wear and tear, which is important for applications with high friction or abrasion.
How strong is alloy steel?
The strength of alloy steel can vary depending on the specific composition and manufacturing process used. Alloy steel typically has higher strength and hardness than standard carbon steel due to the addition of alloying elements like chromium, nickel, or molybdenum. These elements contribute to the formation of microstructures in the steel that can enhance its strength and durability.
The strength of alloy steel can also be influenced by other factors, such as the heat treatment process used and the shape and size of the steel. At Huaxia-steel, we offer a wide range of high-quality alloy steel products that are designed to meet the needs of heavy-duty applications. Our alloy steel products are rigorously tested to ensure their strength and durability, and they meet international standards and specifications. Whether you need alloy steel for construction, manufacturing, or other industrial applications, we have the products and expertise to meet your requirements.
Does alloy steel rust easily?
The answer to whether or not alloy steel rusts depends on the specific composition of the alloy. Some alloy steels contain elements like chromium, nickel, or molybdenum that improve the steel’s resistance to rust and corrosion. These elements can create a protective layer on the surface of the steel that helps prevent rust from forming.
However, not all alloy steels are rust-resistant, and some may still rust if exposed to the elements for extended periods. It’s important to select the right alloy steel for your application to ensure that it has the necessary rust and corrosion resistance.
Does alloy steel rust easily?
The answer to whether or not alloy steel rusts depends on the specific composition of the alloy. Some alloy steels contain elements like chromium, nickel, or molybdenum that improve the steel’s resistance to rust and corrosion. These elements can create a protective layer on the surface of the steel that helps prevent rust from forming.
However, not all alloy steels are rust-resistant, and some may still rust if exposed to the elements for extended periods. It’s important to select the right alloy steel for your application to ensure that it has the necessary rust and corrosion resistance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
⭐ Is alloy steel good?
Yes, Alloy steel is an excellent choice for many industrial applications due to its exceptional strength, durability, and versatility.
It is made by adding other elements to carbon steel to enhance its properties, such as strength, toughness, and resistance to wear and tear.
The specific properties of alloy steel depend on the type and amount of elements added during the manufacturing process.
For example, adding chromium, nickel, or molybdenum can increase the steel’s resistance to rust and corrosion, while adding tungsten or vanadium can improve its strength and wear resistance.
⭐ Is alloy steel strong?
Yes, alloy steel is known for its high strength and durability.
It is a type of steel that contains additional alloying elements other than carbon, which can increase its strength, toughness, and wear resistance. The specific strength of alloy steel can vary depending on the composition and processing of the alloy, but generally, it is stronger than non-alloyed steel. Alloy steel is often used in high-stress applications where strength and reliability are critical, such as in the construction of machinery, tools, and industrial equipment. It is also commonly used in the automotive and aerospace industries, where the strength-to-weight ratio of materials is a significant factor in design. So, if you’re looking for a strong and reliable material for your project, alloy steel is definitely worth considering.
⭐ Is alloy steel magnetic?
Alloy steel can be magnetic or non-magnetic, depending on its composition. Some alloy steels contain elements like nickel, cobalt, and iron, which are magnetic, while others may contain non-magnetic elements like aluminum and titanium.
In general, low alloy steels are more likely to be magnetic than high alloy steels. However, there are exceptions to this rule, and it ultimately depends on the specific composition of the alloy.
Whether or not an alloy steel is magnetic does not necessarily impact its performance or strength. It is simply a property of the material that may be relevant for certain applications or industries. Therefore, it’s important to consider the specific needs of your project when selecting an alloy steel, and to work with a knowledgeable supplier who can help guide you towards the most suitable material for your needs.
⭐ Is 4140 alloy steel magnetic?
4140 alloy steel is a low alloy steel that contains chromium, molybdenum, and manganese. It is widely used in applications requiring high tensile strength, good toughness, and wear resistance.
As for its magnetic properties, 4140 alloy steel is generally considered to be magnetic due to its high iron content. However, the magnetic properties of 4140 steel can be affected by factors such as heat treatment and the presence of other elements such as nickel.
In general, the magnetic properties of alloy steel are not a significant factor in most applications, but it is important to consider when working with magnetic materials or in applications where magnetic interference could be a concern. Overall, 4140 alloy steel is a popular and versatile material with excellent mechanical properties that make it suitable for a wide range of applications in various industries.
⭐ Is alloy steel rust-proof?
Alloy steel contains varying amounts of different metals such as chromium, nickel, and manganese, among others, to enhance its mechanical properties.
While some of these alloying elements can increase corrosion resistance, alloy steel is not completely rust-proof. The degree of rust resistance depends on the specific alloy and its composition. For example, stainless steel is a type of alloy steel that contains a high amount of chromium, which forms a protective layer on the surface, making it highly resistant to corrosion.
However, other types of alloy steel, such as low alloy steel, may not have the same level of corrosion resistance as stainless steel. It’s important to note that while alloy steel may have improved corrosion resistance compared to carbon steel, it still requires proper maintenance and protection to prevent rust.
⭐ Does alloy steel tarnish?
Alloy steel is a type of steel that is made by combining different metals or materials to enhance its properties, such as strength and corrosion resistance.
Whether or not alloy steel tarnishes depends on the specific alloy and environmental factors it is exposed to. In general, high-quality alloy steel is less likely to tarnish than lower-grade alloys, but exposure to harsh chemicals, moisture, and other corrosive elements can cause tarnishing over time.
To prevent tarnishing, it is important to properly maintain and care for your alloy steel products, such as regular cleaning and applying protective coatings. Additionally, selecting the right alloy steel for your specific application and environment can help to minimize the risk of tarnishing and ensure long-lasting performance.
How to cut alloy steel?
There are several methods to consider. The most common way is to use a saw with a high-speed steel blade. This blade can cut through the tough surface of alloy steel and produce precise cuts. Another method is to use a plasma cutter, which uses a high-temperature jet of gas to cut through the metal. This technique is ideal for thicker pieces of alloy steel.
If you need to make curved cuts or intricate designs, a water jet cutter is an effective tool. This machine uses a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive materials to create precise cuts. Additionally, laser cutting can be used to produce clean, precise cuts with minimal material waste.
As a professional alloy steel exporter, our company has extensive experience in cutting and processing alloy steel materials. We work with reliable factories and use advanced equipment to ensure the highest quality products. Contact us for more information on alloy steel cutting and our products.
Can you weld alloy steel?
&
How to weld alloy steel?
Yes, you can weld alloy steel, but the welding process requires more expertise and specialized techniques than welding carbon steel.
It is essential to select the appropriate welding method based on the type of alloy steel, thickness, and intended use of the product. Some of the common welding techniques used for alloy steel welding are Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), and Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW). The selection of filler material and pre-heating temperature is also critical to ensure a successful weld.
When welding alloy steel, it is essential to ensure that the welding environment is free from contamination, including moisture, oil, and dirt. Pre-cleaning the material is necessary to prevent the formation of cracks, porosity, or other defects in the final product.
In summary, welding alloy steel requires specialized expertise and knowledge to ensure a successful outcome. Our company has years of experience in sourcing and supplying high-quality alloy steel products to our clients worldwide. Our team of experts has the necessary knowledge and skills to help you with all your welding needs, ensuring that you receive the best possible quality products and services.
Which aws specification covers electrodes used for welding low-alloy steels?
The American Welding Society (AWS) provides specifications for welding materials and processes.
The specification that covers electrodes used for welding low-alloy steels is AWS A5.5. This specification covers a range of low-alloy steel electrodes that are used for different welding applications, including joining, surfacing, and repair.
The AWS A5.5 specification includes specific requirements for the chemical composition, mechanical properties, and testing of the electrodes to ensure they meet the quality standards for welding low-alloy steels. As a professional alloy steel supplier, we understand the importance of using the correct welding materials and processes to ensure the quality and durability of the final product. We are committed to providing our customers with high-quality alloy steel products and expertise on welding and other related topics.
How to heat treat 4140 alloy steel?
Heat treating 4140 alloy steel involves a specific process to achieve the desired mechanical properties. First, the steel is heated to a specific temperature, then quenched in oil or water to rapidly cool it down. This step is followed by tempering, which involves reheating the steel to a lower temperature to relieve stress and improve toughness. The exact temperature and duration of each step will depend on the desired properties and the specific application. It is important to follow proper heat treating procedures to ensure that the steel meets the required specifications.
As a professional B2B trading company, we have experience in sourcing and supplying high-quality 4140 alloy steel and can provide guidance on the appropriate heat treating methods.
What is alloy steel used for?
Alloy steel is a type of steel that is alloyed with other elements such as chromium, nickel, molybdenum, or manganese. This creates a metal with superior strength, toughness, and durability, making it ideal for a wide range of applications.
- Automotive Industry:
Alloy steel is commonly used to make various automotive parts such as crankshafts, gears, and axles due to its high strength and wear resistance. - Aerospace Industry:
Alloy steel is used to make various aircraft components such as landing gear, engine parts, and structural components because of its ability to withstand high stress and extreme temperatures. - Construction Industry:
Alloy steel is used to make structural components such as beams, columns, and reinforcing bars due to its high strength and durability. - Oil and Gas Industry:
Alloy steel is commonly used in the oil and gas industry for applications such as pipelines, drill bits, and valves due to its ability to withstand high pressure and corrosive environments. - Tool and Die Making:
Alloy steel is used to make various cutting tools such as drill bits, saw blades, and machining tools because of its hardness and wear resistance. - Medical Industry:
Alloy steel is used to make various surgical instruments and implants due to its biocompatibility and corrosion resistance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
⭐ Is alloy steel safe for cooking?
Alloy steel is not recommended for cooking applications.
While it is a strong and durable material, it is not designed for food safety and can contain harmful chemicals or contaminants that may transfer to food.
Additionally, alloy steel is not resistant to corrosion and can rust over time, which can also be harmful to food safety.
For cooking purposes, it is recommended to use materials that are specifically designed for food safety, such as stainless steel or ceramic cookware.
As a B2B trading company focused on exporting alloy steel, our expertise lies in providing high-quality materials for industrial and manufacturing applications, not for consumer food products.
⭐ Are steel wheels better than alloy?
When it comes to wheels, both steel and alloy have their pros and cons.
Steel wheels are generally less expensive and more durable, making them a popular choice for commercial and heavy-duty vehicles. They are also less likely to crack or bend than alloy wheels.However, steel wheels tend to be heavier than their alloy counterparts, which can negatively impact fuel efficiency and handling.
Alloy wheels, on the other hand, are often preferred for their sleek and modern appearance. They are also lighter than steel wheels, which can improve a vehicle’s performance and fuel economy. However, alloy wheels are typically more expensive and can be more prone to cracking or bending than steel wheels, particularly if they are subjected to rough terrain or harsh driving conditions.
Ultimately, the choice between steel and alloy wheels depends on the specific needs and preferences of the vehicle owner.
⭐ Are alloy rims better than steel?
Alloy rims and steel rims each have their own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the specific needs of the vehicle and driver.
In general, alloy rims are more lightweight and offer better performance and handling, while steel rims are more durable and resistant to damage.
However, alloy rims may be more expensive and susceptible to cracking, while steel rims may be heavier and less aesthetically pleasing.
Ultimately, the choice between alloy and steel rims will depend on the specific requirements and preferences of the driver.
As a professional B2B trading company specializing in alloy steel, we can provide customized solutions and expert advice to meet the needs of our clients. Contact us to learn more about our alloy steel products and services.
Steel VS Alloy Steel
When comparing steel and alloy steel, it is important to understand the key differences between the two materials. Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon, while alloy steel is a type of steel that is made by adding other elements to the base iron-carbon composition. These added elements can include manganese, nickel, chromium, and others, which enhance the strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance of the material.
In terms of applications, steel is widely used in construction, automotive manufacturing, and consumer products, due to its strength and durability. Alloy steel, on the other hand, is often used in more demanding applications that require greater strength, such as aerospace, defense, and industrial manufacturing. It is also commonly used in the production of specialized tools and equipment, such as drill bits and cutting blades.
One of the key benefits of alloy steel over traditional steel is its improved strength and hardness. This makes it particularly well-suited for high-stress applications that require high levels of durability and resistance to wear and tear. Alloy steel is also more resistant to corrosion, which is particularly important in harsh environments or in applications that involve exposure to corrosive chemicals or liquids.
In summary, while both steel and alloy steel have their own unique properties and applications, alloy steel offers superior strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion, making it an ideal choice for demanding applications in a wide range of industries.
What is the difference
between steel and alloy steel?
Steel and alloy steel are both widely used materials in various industries such as automotive, construction, and manufacturing. While they share some similarities, there are also significant differences between the two.
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon, with a carbon content ranging from 0.2% to 2.1%. It is widely used due to its high tensile strength, durability, and affordability. Steel can be further classified into various types based on its carbon content and properties, such as mild steel, carbon steel, and stainless steel.
Alloy steel, on the other hand, is a type of steel that contains additional alloying elements other than carbon, such as manganese, silicon, chromium, nickel, or molybdenum. The addition of these elements provides alloy steel with improved properties such as increased strength, toughness, and resistance to corrosion and wear. Alloy steel can be further classified into various types based on its alloying elements, such as low alloy steel, high alloy steel, and tool steel.
One of the primary differences between steel and alloy steel is their composition. Steel is primarily composed of iron and carbon, while alloy steel contains additional alloying elements. This difference in composition results in different mechanical and chemical properties, making alloy steel superior to plain carbon steel in many applications.
Another significant difference between steel and alloy steel is their strength. Alloy steel is generally stronger and tougher than steel due to the addition of alloying elements, making it ideal for high-stress applications such as construction and engineering.
In conclusion, while both steel and alloy steel share some similarities, alloy steel has several advantages over plain carbon steel due to the addition of alloying elements, making it stronger, tougher, and more resistant to corrosion and wear.
What is steel an alloy of ?
Steel is an alloy primarily made up of iron with a small percentage of carbon. However, the exact composition of steel can vary widely depending on the desired properties of the final product, and it often contains other elements as well, such as manganese, nickel, chromium, and molybdenum.
These additional elements can alter the properties of the steel, making it stronger, more durable, or more resistant to corrosion, among other things. For example, adding nickel and chromium can create stainless steel, which is highly resistant to rust and corrosion. Molybdenum is often added to improve the strength and toughness of the steel, making it suitable for use in high-stress applications like aircraft components or industrial machinery.
Overall, the exact composition of steel is carefully engineered to meet specific needs in a variety of industries, including construction, automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. The versatility and strength of steel make it an essential material in modern society, and its importance cannot be overstated.
Is alloy lighter than steel?
Alloy steel and steel have different compositions, which can affect their weight. Alloy steel is made by combining iron with other metals, such as nickel, chromium, or manganese, to produce specific mechanical properties. On the other hand, steel is an alloy of iron and carbon, where the carbon content ranges from 0.05 to 2.0%.
Generally speaking, alloy steel is denser than steel, meaning it has a higher mass per unit volume. However, some specific alloys may be lighter than certain steel grades due to their lower density. For example, aluminum alloys have a much lower density than steel, making them ideal for applications requiring lightweight materials.
It is essential to note that the weight of a material is only one factor to consider when selecting the appropriate material for a given application. Other factors include mechanical properties, durability, corrosion resistance, and cost.
In conclusion, while some alloy steels may be lighter than certain steel grades, the weight difference may not be significant. When selecting between the two materials, it is crucial to consider all relevant factors to ensure the chosen material meets the specific application’s requirements.
Is steel alloy?
Steel is an alloy, which means it is composed of two or more different elements, typically with the primary element being iron. Carbon is a common alloying element in steel and can significantly alter its properties. Other common alloying elements include manganese, nickel, chromium, and molybdenum.
The alloying elements in steel can change its strength, hardness, ductility, and other mechanical properties. For example, adding more carbon to steel increases its hardness, but decreases its ductility. Adding chromium can increase the steel’s resistance to corrosion.
Because steel is an alloy, it can be tailored to meet specific performance requirements for various applications. This makes steel an ideal material for a wide range of industries, including construction, transportation, energy, and manufacturing.
In summary, steel is an alloy composed of iron and other elements, typically carbon, and its properties can be tailored by adjusting the types and amounts of alloying elements used.
Is steel an alloy of iron?
Yes, steel is an alloy of iron. Steel is made up of iron combined with small amounts of carbon and other elements such as manganese, silicon, and sulfur. The carbon content in steel can range from 0.2% to 2.1%, depending on the grade and intended use of the steel. The addition of these other elements can modify the properties of the steel, such as increasing its strength or improving its corrosion resistance.
Iron itself is a metal that is abundant in the Earth’s crust and is commonly used in construction, machinery, and manufacturing. However, iron is relatively soft and weak, and so it is often combined with other elements to create alloys that have improved properties for various applications.
Steel is one of the most commonly used metals in the world, thanks to its durability, strength, and versatility. It is used in a wide range of industries, including construction, automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. Its ability to be modified through alloying and heat treatment makes it possible to create a wide range of grades with different properties, allowing steel to be used in a variety of applications.
Is alloy steel stronger than steel?
Alloy steel is a type of steel that contains additional elements, such as manganese, silicon, copper, nickel, chromium, and other trace elements, to improve its strength, durability, and other properties. Due to the presence of these additional elements, alloy steel has superior strength, hardness, and resistance to wear and tear, making it an ideal choice for heavy-duty applications, such as construction equipment, aircraft, and automotive components.
In comparison to regular steel, alloy steel is generally stronger and more durable. The additional elements in alloy steel improve its mechanical properties, such as tensile strength, yield strength, and toughness, allowing it to withstand more stress and strain without deforming or breaking. Alloy steel also has excellent corrosion resistance, which makes it a great choice for applications in harsh environments, such as marine or chemical industries.
Overall, while steel is a versatile material that has many applications, alloy steel is a stronger and more durable type of steel that is better suited for heavy-duty applications. Its enhanced properties make it a popular choice for demanding industries that require high performance and reliability.
Is alloy better than steel?
When it comes to the debate of whether alloy is better than steel, the answer isn’t a simple one. It depends on the specific application and the qualities that are desired.
Alloy is a mixture of two or more metals, while steel is an alloy of iron and carbon. One of the key differences between the two is that steel is generally stronger than most alloys. However, alloy can have specific qualities that make it better suited for certain applications.
For example, some alloys are more resistant to corrosion than steel, making them ideal for use in harsh environments or outdoor applications. Other alloys can have higher tensile strength, making them ideal for use in applications where weight is a concern, such as in the aerospace industry.
Another advantage of alloy is that it can be customized to meet specific needs. The combination of different metals and their ratios can be adjusted to achieve desired characteristics, such as increased hardness, improved ductility, or better machinability.
In summary, there is no clear winner in the alloy vs steel debate. It all depends on the specific application and the desired qualities. While steel is generally stronger, alloy can offer specific qualities that make it a better choice for certain applications. Ultimately, it’s important to work with a knowledgeable supplier who can help you determine the best material for your specific needs.
Carbon Steel VS Alloy Steel
Carbon steel and alloy steel are two popular materials used in various industries. Carbon steel is an alloy of iron and carbon, while alloy steel is made up of iron, carbon, and other elements such as manganese, nickel, chromium, and molybdenum.
The main difference between the two is that alloy steel has additional alloying elements that enhance its mechanical properties, such as strength, toughness, and wear resistance. Carbon steel is known for its hardness and durability, while alloy steel is often used for its high strength and corrosion resistance.
Both materials have their own unique advantages and applications, and the choice between the two will depend on the specific needs and requirements of the project.

VS

Stainless Steel VS Alloy Steel
Stainless steel and alloy steel are both popular materials in various industries, including manufacturing, construction, and aerospace. While both materials share similar properties, there are significant differences between them.
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron, chromium, and sometimes other elements like nickel or molybdenum. It is known for its corrosion resistance, making it a popular choice in applications where exposure to moisture or chemicals is common. Stainless steel is also known for its durability, strength, and aesthetic appeal.
On the other hand, alloy steel is made by mixing iron with other elements like nickel, chromium, or molybdenum. Alloy steel has improved properties compared to regular steel, including greater strength, hardness, and wear resistance. It is often used in applications that require high strength and toughness, such as machinery parts, toolmaking, and construction.
In terms of cost, stainless steel is generally more expensive than alloy steel due to its corrosion-resistant properties. However, the increased strength and durability of alloy steel can make it more cost-effective in certain applications.
Ultimately, the choice between stainless steel and alloy steel depends on the specific application and required properties. Companies that work with these materials should carefully consider the benefits and drawbacks of each and consult with industry experts to make informed decisions.

VS

Is alloy better than stainless steel?
Alloy steel is known for its high strength and toughness. It is often used in applications that require high stress and wear resistance, such as in construction and engineering. Stainless steel, on the other hand, is known for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. It is commonly used in applications that require cleanliness and sanitation, such as in the food and medical industries.
When comparing alloy steel and stainless steel, it is important to consider the specific application and requirements of the project. While alloy steel may be stronger and tougher, it may not be as resistant to corrosion as stainless steel. Conversely, while stainless steel may be more corrosion-resistant, it may not have the same level of strength and toughness as alloy steel.
Ultimately, the choice between alloy steel and stainless steel depends on the specific needs of the project. A professional and experienced supplier can help guide the decision-making process and ensure the optimal material is chosen.
Request A Free Quote
We’d like to work with you
If you require further information about our metal sheet products or architectural projects, please don’t hesitate to leave your contact details and message here.
Our team of experts will respond within 24 hours to continue the discussion and provide you with any additional information you requires.